Collagen benefits make you ensure you’re getting enough either by eating collagen foods or the right nutrients that help your body produce more of it naturally. The reason there are so many healthy collagen benefits is because it is our most abundant protein.

About 70% of the protein in our bodies is made from collagen. Exactly, what is collagen good for? This article I hope answers this question for you. Collagen serves many purposes, and is good for many health related things. It actually holds us together like glue.
Its name comes from the Greek “kólla” which means “glue.”
Desirable collagen benefits for skin are just one of many. Collagen benefits range from keeping your skin elastic and youthful, your muscles strong and intact, your brain alert into old age, and your gut healthy and free from leaky gut syndrome and other digestive complications.
Collagen benefits are attained in several ways:
- You can eat it directly (fresh bone broth, collagen supplements)
- Produce it endogenously by eating certain nutrients that help with collagen synthesis
- Or you can even apply it topically with its beauty product related applications
From rich, slow cooked bone broths, to homemade collagen ingredient dessert recipes, to producing it naturally via consumption of certain vitamins and nutrients, there are several ways to ensure sufficient collagen.
Before we jump into the full list of collagen benefits, let’s quickly go over what collagen is, where it comes from, and how we normally attain its benefits.
Table Of Contents:
What Are The Collagen Benefits?
But first, what is collagen?
You, your dog and all the lovely dolphins of the sea are all made up of a large percentage of collagen.
It’s the single most plentiful protein amongst mammals.
According to Medical News Today, collagen is a,
…hard, insoluble and fibrous protein that makes up one-third of the protein in the human body.
Collagen is a long chain amino acid with its highest content in the connective tissues, bones and skin.
Quoting Molecular Cell Biology,
Collagen is the major insoluble fibrous protein in the extracellular matrix and in connective tissue.” (Think, chicken feet or rat tails).
Continued…
Collagen molecules pack together to form long thin fibrils of similar structure…numerous epithelial cells make certain types of collagens. The various collagens and the structures they form all serve the same purpose, to help tissues withstand stretching.
Below is an informative video by Dr. Justin Marchegiani. He goes over several collagen benefits and what collagen is.
There are over 16 different types of collagen, most coming from the first three types.
Over 90% of the collagen in the human body is Type 1 Collagen.
Common Collagen Types (source):
- Collagen Type 1: Skin, tendons, vasculature, organs, bones
- Collagen Type 2: Cartilage (main collagenous component of cartilage)
- Collagen Type 3: Reticulate (main component of reticular fibers), commonly found alongside type I
- Type 4: Forms basal lamina, the epithelium-secreted layer of the basement membrane.
- Type 5: Cell surfaces, collagen for hair and placenta
What Is Collagen Made Of?

Sheep skin (ovine) is one of the many animal sources of collagen
Collagen can be attained from animal, marine and vegetable sources. The main sources of collagen are land animals and birds.
According to Wiley Online Library,
“Animal terrestrial sources comprise from chicken, kangaroo tail, rat tail tendons, duck feet, equine tendon, alligators bon/skin, bird’s feet, sheepskin, and frog skin.”
Land Animal Sources Of Collagen:
- Bovine collagen (cows): Bone, cartilage and skin of cow is used. It has many industrial ad medical uses including capsules for nutritional supplements, hernia repair and reconstructive or plastic surgeries.
- Porcine (pig): Bone, cartilage and skin are used. Porcine collagen is the most similar to human collagen, so it creates the least allergenic response of the land animal collagens.
Those are the two main animal collagens. Here are more (2):
- chicken collagen
- kangaroo tail
- rat tail tendon
- duck feet
- horse tendon (equine)
- bird feet
- alligator skin and bone
- sheep skin (ovine)
- frog skin
- egg collagen
The problem with land animal sources of collagen is that they can be allergenic and unsustainable. Due to these issues (and the potential for contamination and disease), the search for equally effective, non animal collagen sources has been on its way for some time with some success.
Marine Sources Of Collagen:
- marine animal bones
- fins
- fresh water fish scales
- saltwater fish scales
- starfish
- jellyfish
- sponges
- sea urchin
- octopus
- squid
- cuttlefish
- sea anenome
- prawn
One fish collagen benefit is that the parts used are usually considered waste, meaning less environmental pollution because the waste is what’s needed for the fish collagen production. One man’s trash is another’s treasure, right? The “waste” used to produce collagen from fish are their bones, skin, fins and scales.
These are some of the marine animals used over land animal sources due to their greater absorption rates “due to low molecular weight, and an almost negligible presence of biological contaminants and toxins.” (source)
More Benefits From Marine Collagen
- very low presence of biological contaminants and toxins
- low inflammatory response
- no risk of disease transmission (this has more potential with land animal collagens)
- high yield, more sustainable:
This table here below shows the yield amounts
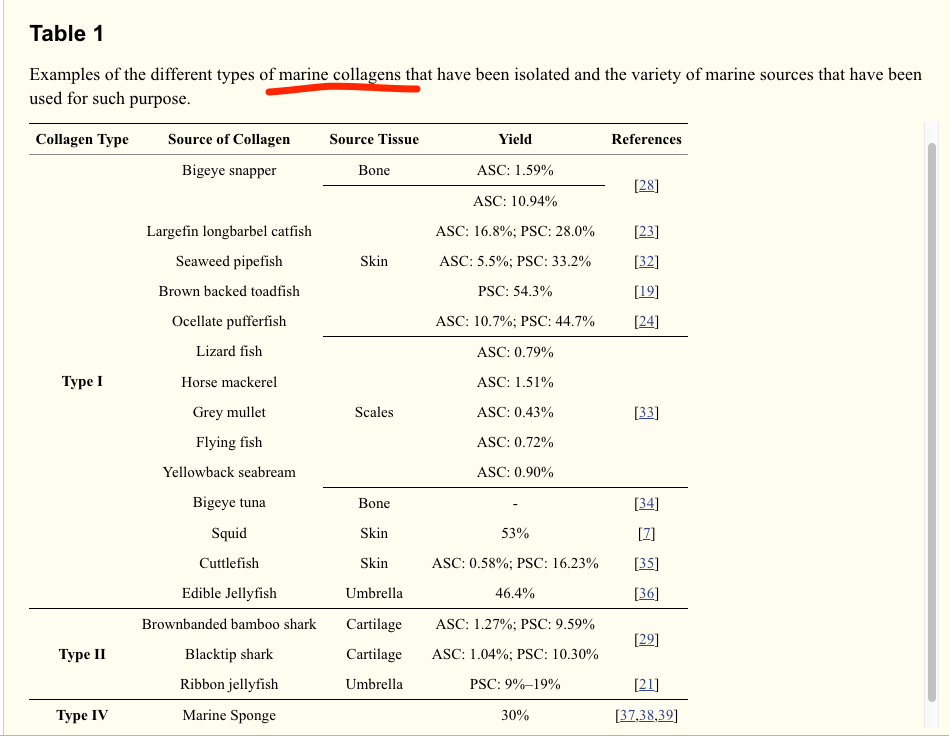
Source: Marine Origin Collagens – NIH
The downside of these benefits of collagena – as some call it – are that marine collagen may not be as effective. Here’s a quote from a journal review of collagen by Maria Rodriguez MRS describing why not:
The use of collagen in diverse applications often depends on thermal stability, which is related with body temperature and living environment of the organism. Marine collagen and its low thermal stability limit its applications.
Nutrients That Help Collagen Production
Certain nutrients can help your body synthesize more collagen.
- Sweet potatoes are packed with vitamin A (retinol, beta-carotene) which promotes collagen production. If you’re on a low carb keto diet, and prefer to lay off the sweet potatoes, there are plenty of other keto-friendly vitamin A options; liver, mackerel, goat cheese, butter, feta cheese, kale, spinach, romaine lettuce and grapefruit, to name a few.
- Chlorella is another collagen friendly food. It has a unique nutrient called Chlorella Growth Factor (CGF) which can promote collagen synthesis.
- Or if you’re a berry lover like me (any and all berries!), you’ll be glad to know that berries contain ellagic acid, which has been shown to protect the breakdown of collagen and wrinkled skin from the sun’s UV-B rays on those days you just can’t get enough of the sun’s glorious rays (I’m there with you).
- Any foods with Vitamin C also help promote collagen synthesis.
If you have a generally healthy lifestyle and your way of eating includes collagen-friendly vitamins and nutrients, you don’t need to supplement it. Chances are you’re already experiencing collagen benefits.
5 Great Collagen Benefits Provided:

1. Arthritis: Osteoporosis & Rheumatoid
Cartilage is rubbery. It covers the ends of your bones in your joints, lessens friction and absorbs shock. Because collagen is one of the main four substances that makeup cartilage (proteoglycans, water and chondrocytes being the other three), it helps make cartilage strong. Not only that, collagen creates a structure within cartilage that helps the other three substances set in place. Cartilage is over 70% water and has no nerves. The water shifts, moves and reabosrbs into it depending on the motion of the joint.
How this relates to arthritis:
Arthritis is joint inflammation. The most common form, osteoarthritis, is basically joint disease. It’s when joint cartilage breaks down and you’ll see this happening most in the knees, hips, finger joints, the base of thumb joint, and even your spine.
Osteoarthritis makes joint cartilage stiff. It destroys the elasticity and sets it up for damage. Cartilage is supposed to absorb shock and more, but if it’s worn away due to natural aging or a reduction of collagen, the ligaments can start hurting and being damaged to the point of bone touching bone.
One treatment used for osteoarthritis is the combo of glucosamine sulfate and chondroitin sulfate supplements; they’re part of cartilage. These two components, as explained on WebMD, “are the building blocks for proteoglycans and appear to stimulate chondrocytes to make new collagen and proteoglycans. The supplements are well-tolerated and safe.”
And thus, collagen plays an important role in healthy joint cartilage. One PubMed article describes a review on the current status of collagen hydrolysate in the treatment of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis. What they did was reviewed all the literature out there on the subject as well as the clinical studies and trials. They concluded,
Collagen hydrolysate is of interest as a therapeutic agent of potential utility in the treatment of osteoarthritis and osteoporosis. Its high level of safety makes it attractive as an agent for long-term use in these chronic disorders.
Another study on athletes and activity-related joint pain found collagen benefits them significantly. This was the first clinical trial that lasted 24-weeks and concluded that athletes who took collagen hydrolysate as a supplement had significantly significant beneficial changes compared to the placebo group. They tested several aspect of joint pain, from different movements to pain when at rest.
There are currently many studies underway to prove how collagen benefits both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. You can read about some of the current trials on collagen and arthritis in the links provided below:
- 4 Trials on collagen benefits for Rheumatoid Arthritis
- 5 Trials on collagen benefits for Osteoarthritis
2. Collagen for Hair & Skin Health
Collagen holds us together “like glue.” It provides structure to our cartilage, and helps our bones, joints and tendons. But it’s not just the inside where collagen benefits us humans (and all mammals). It also promotes skin elasticity and helps support the integrity of your skin. All sources of collagen will benefit you. Collagen benefits skin, hair and nails.
Collagen & Wrinkles
Wrinkles and cartilage issues are age related problems that come over time as part of the natural aging process. Women can even lose up to 60% of collagen production after menopause. Because our bodies produce less collagen with age, skin loses elasticity, and we get wrinkles. Our joints start to feel it too because cartilage loses its strength and flexibility.
Luckily, collagen is able to be produced within our bodies, and also safely used medically in order to make up for diminished production that comes with the natural aging.
The cosmetic industry LOVES collagen. And for good reason. It’s safe, and it helps all kinds of skin aging conditions. Skin aging in inevitable. A healthy older person usually wears his wrinkles very well. It would be weird to see an older person with zero wrinkles. It’s natural. And in my opinion, there’s a novelty to it. I’m in my 30’s, and I wear my new wrinkles around my eyes with pride. When I flex my biceps, there’s a new crease there that I never had before. It might be because I drive a motorcycle in the hot sun everyday with a short sleeved shirt, but that’s ok.
How Collagen Benefits Aging Skin:
Skin aging occurs when collagen fibers become damaged, thinned or weakened. For this reason, collagen eye masks, creams, supplements and many medical procedures cartilage regeneration or skin grafts use collagen as an anti aging solution.
According to a post by a great nutrition and health blog I like to read called Self Hacked, “UV radiation activates several cell growth factors and cytokine receptors, which increases MMP (matrix metalloproteinase) production and decreases collagen type 1 production.”
Collagen 1 is the skin, tendons, vasculature, organs, and bones type. Collagen Type 1 is the most vital collagen. There is no doubt about how it helps your skin retain its youthful elasticity. As you age, the fine lines start to form, skin dries easier and becomes loose.
Studies on Collagen & Skin Aging
- In this double-blind, placebo-controlled study, skin elasticity improvement in women women between the ages of 35 and 55 was noticeable within 4 weeks!
- In this 2014 study on the oral intake of bioactive collagen peptides, a reduction of wrinkles and an increase in dermal matrix synthesis had a major positive outcome on skin wrinkles after just 8 weeks of taking the collagen supplement.
The benefits of collagen on skin are proven.
The question is, should you supplement it? With how safe it is, in my opinion it doesn’t hurt. I’d choose the lifestyle and collagen friendly food route first, followed by high quality collagen supplementation. Why not help your youthful glow while fixing your joints at the same time?
3. Collagen, Blood Sugar & Diabetes
Diabetics lose collagen faster than the average person.
Part of the aging process is the loss of collagen. Over time we produce less and less. This is what leads to natural aging like wrinkles and loose skin, and the more impactful ones like weakened joints and bones. Not only does collagen benefit your skin and your joints, but it goes as far as helping your blood sugar as well. Yes, eating chicken feet can help reverse your diabetes.
For example, apple cider vinegar reduces the glycemic load of food. It blunts the blood sugar impact of sugary foods if you drink some before you eat. In the same way, collagen may be able to help. In a video I post below by Christ Masterjohn PhD, he goes over 7 “hacks” to control your blood glucose after meals. Consuming vinegar before you eat is one of them. And so is collagen.
He says to consume 3 to 5 grams of glycine before you eat. Here’s where the collagen part comes in. To get 3 to 5 grams of glycine, you can get it in a few different ways:
- Pure glycine powder: cheap, sweet tasting.
- Collagen or gelatin: hydrolyzed collagen peptides are one of the best options. He states that 3 to 5 grams of glycine to benefit your blood sugar would require around 10 to 15 grams of hydrolyzed collagen.
- Bone broth: has the same benefit as collagen or gelatin but with added minerals. (10 grams of protein per serving is needed for the 3 to 5 grams of glycine).
More On How Collagen Benefits Blood Sugar:
- Diabetics’ collagen declines faster than others
- Taking a collagen protein supplement or getting it from food can help stabilize blood sugar
- Collagen’s glycine content can assist with proper insulin secretion
4. Detoxification
Another glorious health benefit from collagen is the fact that it’s a building block in the body’s natural ability to formulate glutathione (GSH). A good natural detox is something we can all use in today’s world of unavoidable toxins coming at us from the air, the water, the food and just life in general.
Collagen protein’s glycine is a precursor amino acid that your body uses to produce glutathione. Hence, getting more collagen via food or supplements supports your body’s natural ability to create glutathione. And glutathione helps your body detox.
The role of glutathione in detoxification
If you want to read about this connection of glutathione and detoxification in pure medical science speak, here’s a PubMed article that will break down how this process works in your body.
And here’s another from CancerTreatmentReviews.com.
Glutathione is an amino acid that is often donned as THE #1 antioxidant.
But the thing is, you need to produce it endogenously. It’s hard to get sufficient amounts from food. Thus, eating foods that are precursors to its formation is key. This is one of the very best collagen benefits and could easily be #1 on this list, even though this list of 10 collagen benefits is in no way in order of importance. They call can be #1. When you eat foods with glutathione in them, the digestion process diminishes its health benefit value. You need to produce it, not eat it.
Liver disease has become an epidemic today. Non alcoholic fatty liver disease is RAMPANT. It’s something I plan to focus on more on this blog as I have personal experience with it and taking simple steps to recover from it have worked as the liver is the only organ that can completely regenerate itself as long as you haven’t reached the scarring point of cirrosis.
Other than being a wonder-detox antioxidant, glutathione can also boost your immune funtion and protect you from excess free radicals.
So if you’re looking to get rid of all the environmental toxins we’re bombarded with today, take advantage of the collagen benefit that is increase glutathione production. Please, if you’re suffering from liver issues (you’ll feel the pain in your upper right abdomen. It’s near your gallbladder), start drinking water with a bit of ACV in it before your meals and consider eating or supplementing collagen protein.
What it comes down to is that glutathione is a great detox antioxidant, and collagen protein helps you produce more of it.
So now that you know about how glutathione helps you detox and how collagen benefits you in that way, here’s a few more non-collagen ways to get more.
More Ways To Increase Glutathione:
- Get more vitamin C
- Eat foods naturally rich in sulfur
- Also eat foods naturally rich in selenium; brazil nuts are one of the best, but make sure they’re not moldy as this can be a problem with brazil nuts. Fish and organ meats will do the trick as well.
- Eat glutathione foods: avocados and asparagus are the two I always shoot for. Spinach too.
- Fit a few whey protein shakes in throughout the week (for the cysteine which helps glutathione production)
- Take a high quality Milk Thistle supplement. Milk thistle can help increase glutathione levels. I’m loving this OmniBiotics brand milk thistle, Liver Reboot (They’re an honest company and do what they can to produce quality nutritional supplements).
5. Digestive Health
Its high glycine levels provide many digestive health benefits. Things like IBS, intestinal permeability or “leaky gut syndrome” among other gastro related issues like heartburn and reflux disease.
In this study on people with inflammatory bowel diseases like ulcerative colitis (UC), Crohn’s disease (CD), on the collagen portion of the study they found that “…serum concentrations of collagen IV are decreased, in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.”
Collagen helps you digest your food better: The amino acids in collagen are good for your gastrointestinal health. The high levels of glycine in collagen are key to improving your digestion. What it does is helps with low stomach acid levels. It increases your stomach acid which is a good thing and it helps your digestive system. That’s where the collagen benefits come from.
More Collagen Benefits: Collagen also helps your brain, your bones, muscles, it helps with cellulite, weight loss and even hair loss.
4 Ways To Avoid Decreased Natural Collagen Production

If you’re not taking care of yourself, you’re malnourished, or are living a harsh lifestyle, you may be hurting your body’s ability to produce collagen naturally. Here are some ways to help turn that around and get you back on the collagen producing train. It’s as simple as changing up some things in your lifestyle and way of eating (WOE).
1. Exercise
To stimulate collagen formation you need to exercise hard and consistently.
If you can’t remember the last time you did a full-on sprint, not just a jog, a sedentary life for a few years can decrease collagen and more. I’ve been there. I went out after a 3 year hiatus to just get out and do a jog or run for a mile or so. I couldn’t do it. It felt like I was tweaking every joint in my ankles with each step and sprinting felt like all joint cartilage was gone. Living a sedentary lifestyle for 3 years after a lifetime of being active and athletic, it is shocking to see what the lack of exercise can do to you.
Eating is not always enough.
Exercise can help your body produce more collagen naturally. It stimulates the natural formation of it. This added collagen protein when in a state of decreased collagen will be great for your skin, your tendons, bones and ligaments, and even your brain and your muscles.
2. Sleep & Stress Reduction
Another important factor in natural collagen production is proper sleep and less stress.
Skin repairs itself by producing more collagen while you sleep.
Sleeping less than 7 or 8 hours per night means less time to repair fine lines and elasticity from the day and overtime less sleep means less collagen for months and years, thus this tends to lead to the fact that it can make you age faster, get more fine lines or wrinkles faster, dry out faster, etc.
Taking a bovine collagen supplement and eating more collagen foods like bone broth can help you sleep. The sleeping itself will help you get more of collagen benefits, and it all works out in the end. Sleep is the key factor.
As far as stress goes, research shows that stress damages your skin collagen integrity. Taking collagen or eating more collagen foods will help battle the consequences of stress on skin collagen.
3. Collagen Producing Foods
Collagen foods that either directly supply it, or provide the nutrients that help you produce more of it naturally are essential. Collagen producing nutrients include vitamin A, vitamin C, and Vitamin B3.
Here’s a list of collagen rich foods:
- #1 Bone Broth
- wild caught fish
- bitter vegetables
- chlorella
- dark green vegetables
- leafy greens
- carrots
- sweet potatoes
- white tea
- tomatoes
- pumpkin seeds
- almonds
- chia seeds (soak in water)
- berries
- kiwi
- eggs
- avocado
- citrus fruits
- garlic
- grass fed meat
- oysters (be careful of raw oyster if you have liver issues)
Bone Broth is the best collagen food source. The joints, tendons and skin in them. If you go for a packaged bone-broth, try to make sure they contain these. They’re what make bone broth an ideal direct source of collagen. Absolutely nothing will top a fresh slow cooked bone broth! Check out our bone broth recipe, it’s a great one!
What About Collagen Supplements?
There are many benefits to using collagen supplements. If you don’t get enough collagen from food, collagen supplements can be really great supplements that are high quality and even better than food sometimes. You have to be careful with collagen supplements because of pesticides and harmful ingredients can potentially contaminate these.
I’ve taken a number of different collagen powders, and the list above shares what I believe are the best out there.
Collagen powder benefits are up there with foods as long as it’s from high quality sources. Collagen products should comes with third party certifications. It’s important to get a quality collagen product. A free-range grass-fed collagen or heavy metal free wild caught North Atlantic fish source.
When choosing collagen supplements and powders, it comes down to finding the most transparency company that labels each ingredient and the source and processes used to create it. If I had to choose one, the very best collagen supplement products out there right now are made by Great Lakes Collagen.
They are the most transparent collagen company, seem very honest, and are also one of the best priced.
There are many sources of collagen that can provide all its health benefits.
All these are wonderful sources of collagen:
- hydrolyzed collagen
- collagen peptides/collagen peptide powder
- collagen hydrolysate
- beef collagen (my favorite)
- marine collagen (another great one)
- liquid collagen
The key is to choose quality.
For bone broth, find grass fed. If you’re going the protein and powder route, choose high quality like Great Lakes. Eating more collagen foods, bone broths and also adding a collagen protein powder into your diet all seem like great natural ways to improve your overall health.
Conclusion: Is collagen good for you?
That one’s a resounding, yes.
As you can see from this article, there are many health benefits of collagen.
It’s easy to get collagen from food.
And it’s easy to find high quality supplements for it too.
At the end of the day, it seems that collagen is not something you want to lack. Thanks for coming by the site. These were the benefits and up next is the top collagen supplements of 2019 review post.
UP NEXT: The 6 Best Collagen Supplements of 2019
We’re also on all the main social platforms, here’s our Instagram and Facebook!
Related Posts:
- Best Keto Supplements (Vitamins & Minerals)
- 4 Black Garlic Benefits, How To Make It, And Where To Buy It
- 9 Fermented Foods Benefits and How To Start Fermenting At Home
- 5 Easy Fermented Food Recipes
(1) Markus J. Buehler Nature designs tough collagen: Explaining the nanostructure of collagen fibrils P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, August 15, 2006
(2) Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science Vol. 5 (03), pp. 123-127, March, 2015 Available online at http://www. japsonline. com



Leave a Reply